
Dog skeleton with major bone elements labeled (Davis, 1987, p. 54;... Download Scientific Diagram
The Anatomage Dog is the first highly detailed dog anatomy atlas that comprehensively features internal organs, including vascular systems and muscular-skeletal structures. Originating from real dog data, the Anatomage Dog exhibits the highest level of anatomical accuracy. All of its volumetric 3D and individual structures are segmented, users.
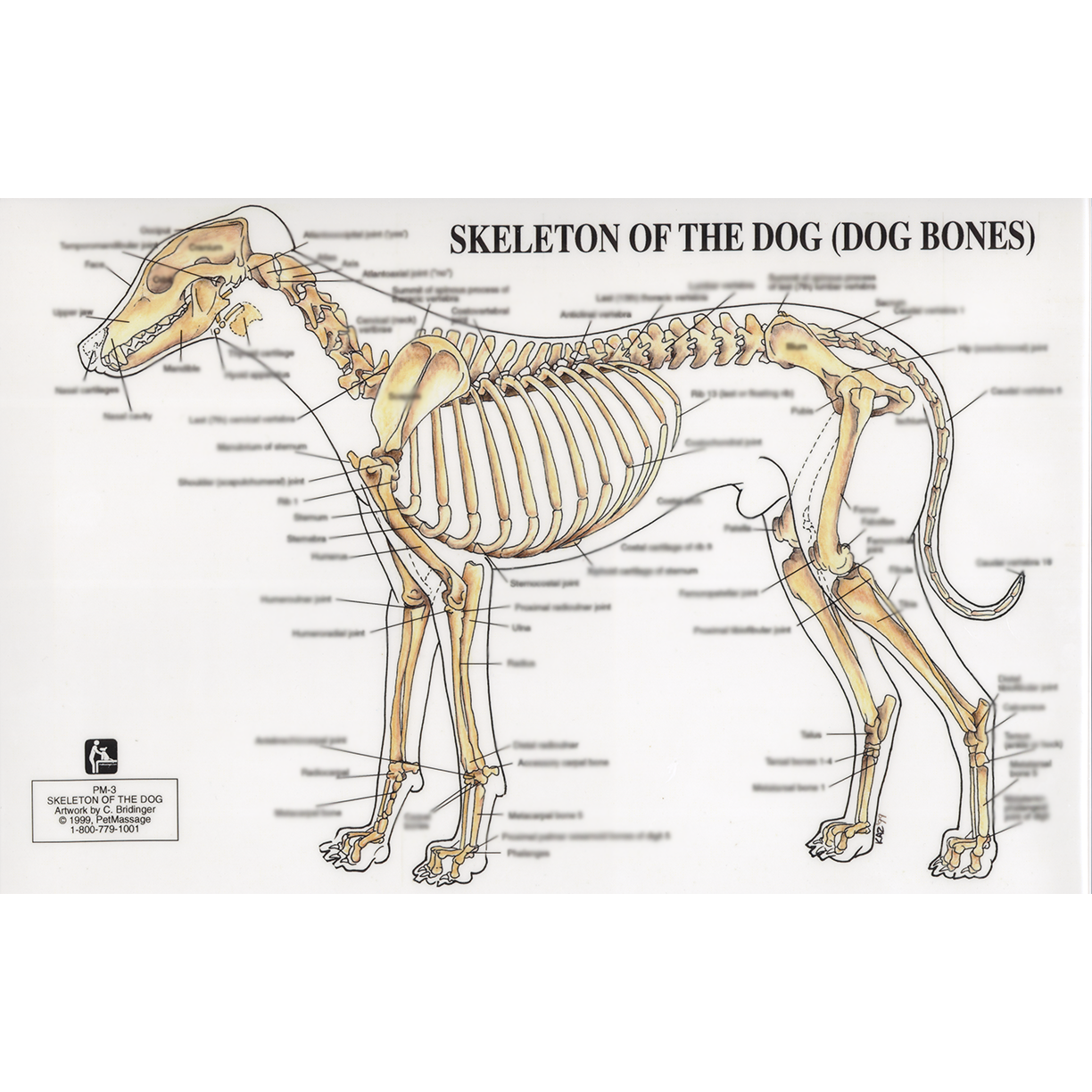
PetMassage™ Chart 3 Skeleton of the Dog · PetMassage™ Training and Research Institute
This veterinary anatomical atlas includes selected labeling structures to help student to understand and discover animal anatomy (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system). Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated.

Labeled Dog Skeleton Diagram
Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length.
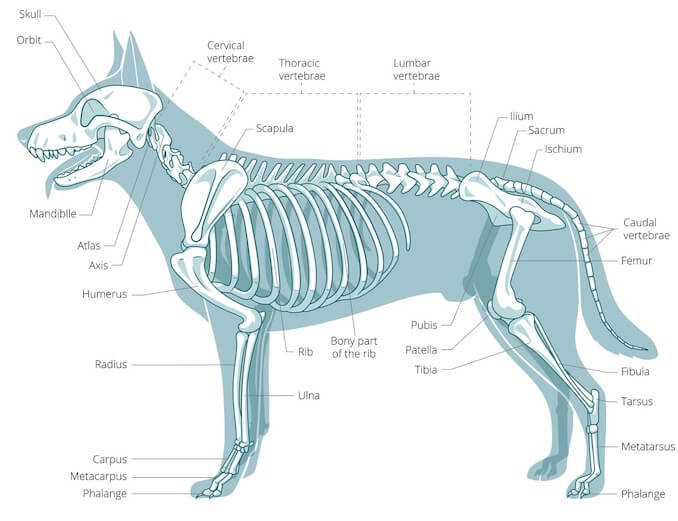
A Visual Guide to Dog Anatomy (Muscle, Organ & Skeletal Drawings) All Things Dogs
In the big picture, the dog skeleton is made of two basic parts: axial and appendicular (limbs). Axial skeleton = head (skull) + the spine (made of vertebrae) + ribs + sternum. Appendicular = forelimb bones + hindlimb bones. The axis of the dog skeleton is composed of the skull, spine (made of vertebrae), ribs and sternum (made of sternebrae).

Anatomy of dog skeleton with labeled inner bone scheme vector illustration Dog skeleton
Our canine charts cover internal organ anatomy, the musculoskeletal system, common pathologies and guides to dog health and safety. Excellent wall displays in vet clinics, surgeries, dog groomers, and veterinary colleges. Our canine posters are s uitable for both animal lovers and veterinary studies.. Our canine model range covers detailed pathology models, common canine parasite models.

Dog Skeleton Anatomy
Components of the Musculoskeletal System in Dogs. Bones provide rigid structure to the body and shield internal organs from damage. They also house bone marrow, where blood cells are formed, and they maintain the body's reservoirs of calcium and phosphorus. Old bone tissue is constantly replaced with new bone tissue in a process called.

Vintage 1935 Dog Veterinary Print Skeleton Of Dog Anatomy Of Dog Canine Skeleton Dog Bones Book
The dog skeleton anatomy consists of bones, cartilages, and ligaments. You will find two different parts of the dog skeleton - axial and appendicular. Here, I will show you all the bones from the axial and appendicular skeleton with their special osteological features. Again, I will provide more labeled diagrams for each dog skeleton bone.

The Canine Skeleton (Digital Download) Nursing Knowhow
Anatomic Planes The main planes of motion for dogs are as follows (see Figure 5-1): • The sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. • The dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions.
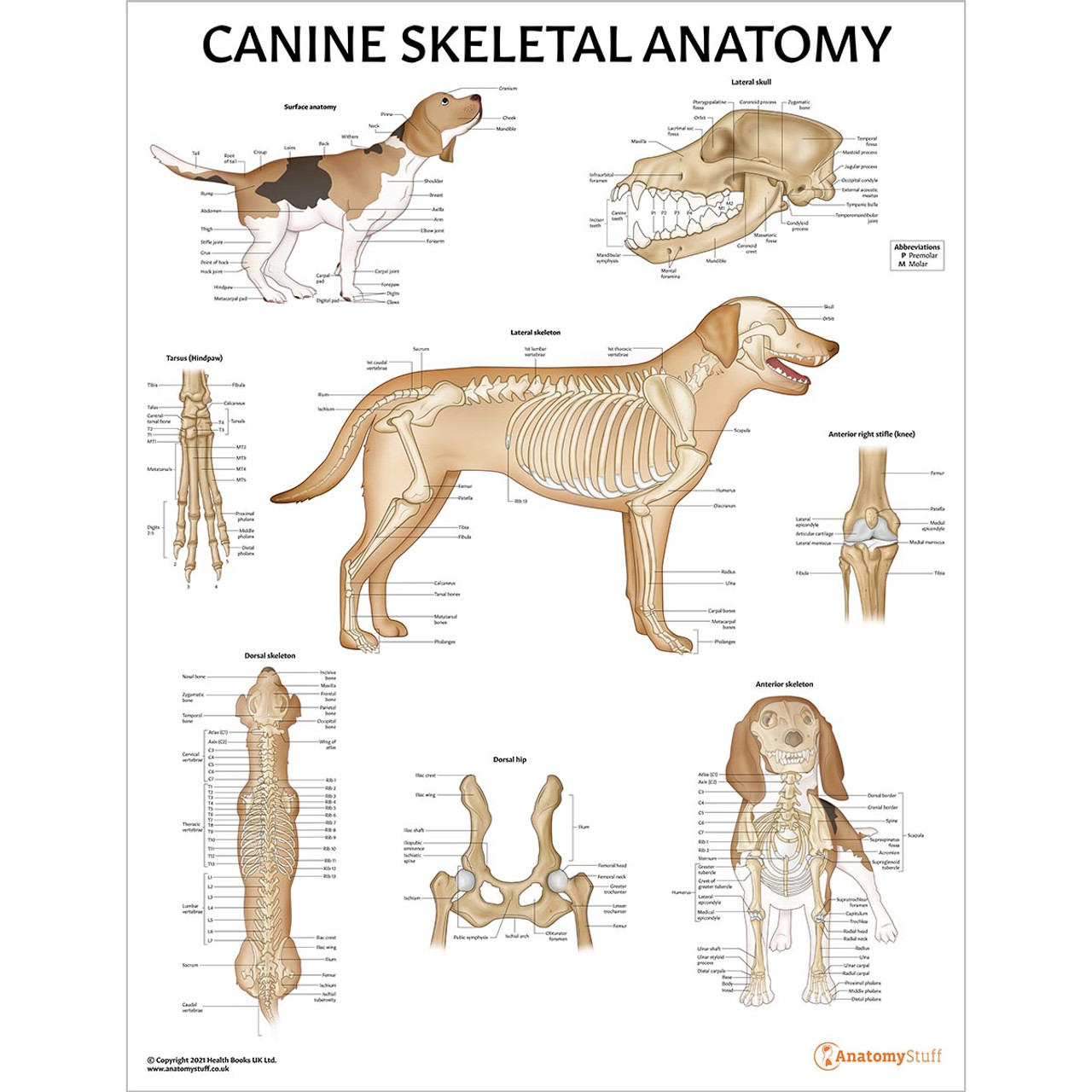
Canine Skeletal Anatomy Laminated Chart Dog Skeleton Poster
A female dog's reproductive system has similar organs as a human's. The female dog anatomy external organ is the vulva, which opens to the vagina. A pregnant female dog's anatomy includes two ovaries, which produce eggs, the cervix, fallopian tubes, and the uterus. The uterus becomes the womb for her puppies during their gestation period.

Canine Anatomical Skeleton Bosley Dog (Large)
The anatomy of a dog includes its skeletal structure, reproductive system, the internal organs, and its external appearance. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better. External Anatomy Dogs, like all mammals, have eyes, a nose, a forehead, and ears.

Anatomy of a male dog crosssection, showing the skeleton and internal organs. Colour process
Summary Anatomy of a Dog Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Would you be surprised to know that short dogs are more aggressive? Or taller dogs are more affectionate?

FileDog anatomy lateral skeleton view.jpg
An overview of the anatomy of the canine skeleton.Follow on twitter @ https://twitter.com/PerkyVetInstagram: Perkydvm
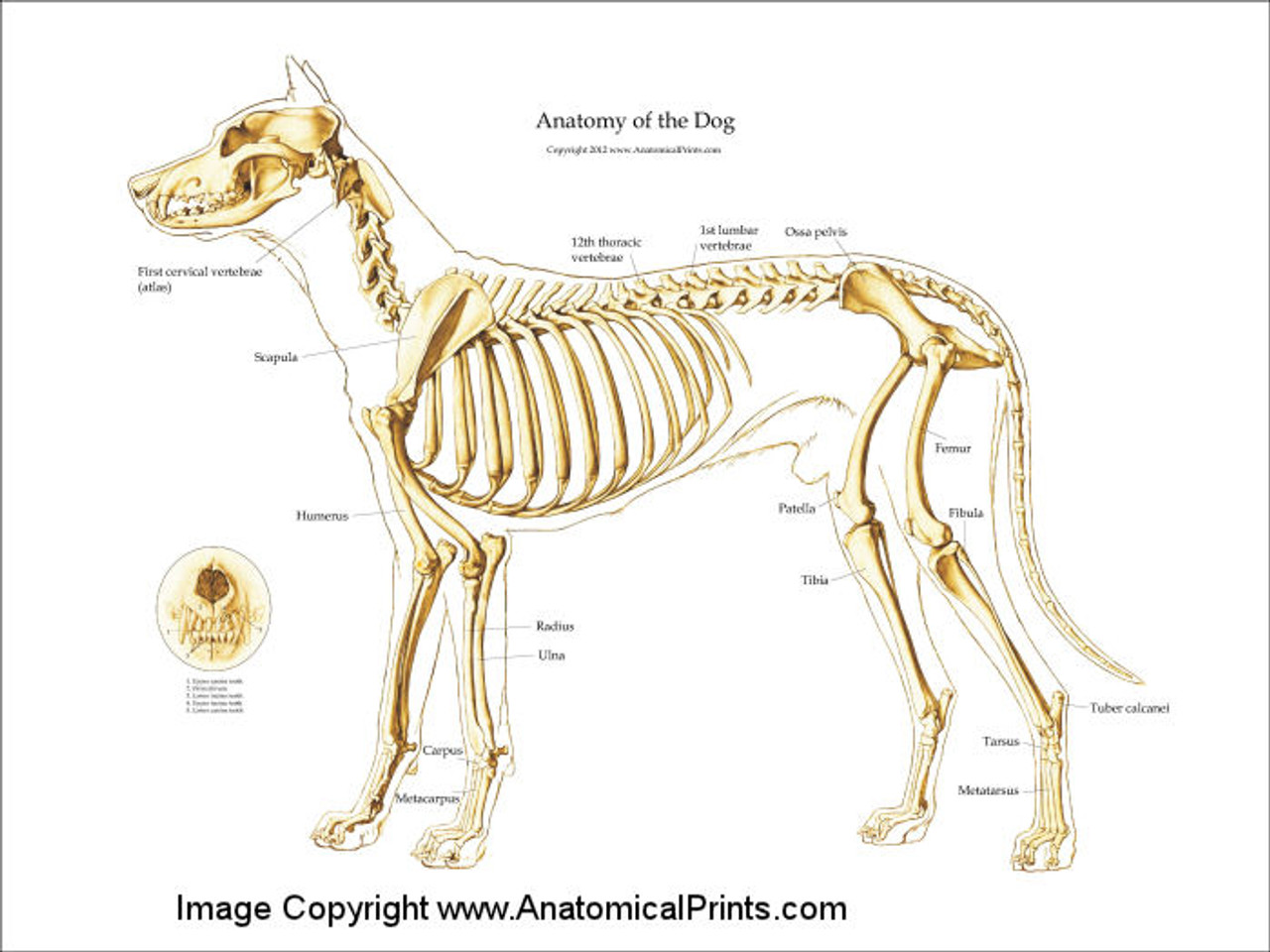
Canine Skeleton Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies
This is an overview of the canine skeleton, pointing out features that help in identification and orientation.If you find this helpful, please let me know by.

maryrosedog Dog skeleton, Dog anatomy, Dog skull
The skeleton is the framework upon which the muscles, tendons, and ligaments are built to provide locomotion for the dog and to serve as a means of protecting the internal organs. For the most part, the composition of the skeleton dictates the movement of the dog.

Dog Anatomy Dog Skelton
How are dog skeletons adapted? Dogs have skeletons disconnected shoulder bones that are very similar to human skeletons. Their spine, skull, and limbs have adapted for their body weight by being sturdier than the same bones in people would be. They also have a light rib cage to run quickly without tiring out too easily.

Skeletal abnormality in dogs and cats
A dog's skeleton is made up of many different bones, which provide structure and support for their body. Dogs have over 300 bones in their body, which is more than humans who have around 206 bones. Their skeleton includes their skull, spine, ribcage and limbs. Dogs have four legs that are designed to help them move quickly and efficiently.